Week 8: Mutation-based and Generation-based black-box fuzzing
Mutation-Based Black-Box Fuzzing
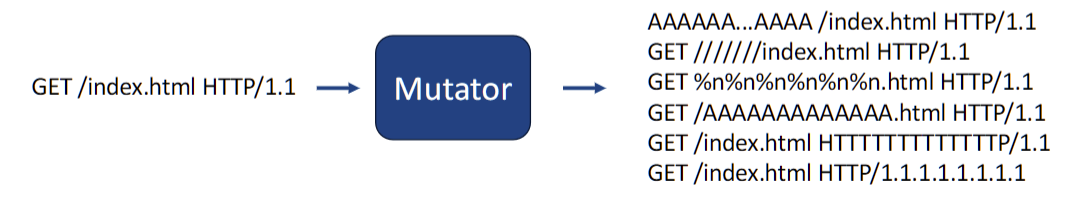 mutation-based fuzzing. The process involves taking one or more valid inputs, known asseed inputs, and applying small changes (mutations) to them to create new test inputs. The diagram shows a valid HTTP request being mutated into many malformed variations. 基于突变的模糊测试涉及获取一个或多个有效输入,称为种子输入,并对其应用小的更改(突变)以创建新的测试输入。该图显示了有效的 HTTP 请求被变异为许多格式错误的变体。
mutation-based fuzzing. The process involves taking one or more valid inputs, known asseed inputs, and applying small changes (mutations) to them to create new test inputs. The diagram shows a valid HTTP request being mutated into many malformed variations. 基于突变的模糊测试涉及获取一个或多个有效输入,称为种子输入,并对其应用小的更改(突变)以创建新的测试输入。该图显示了有效的 HTTP 请求被变异为许多格式错误的变体。
The changes made by the fuzzer are called mutation operators. These can be:
- Low-level and generic: Such as flipping bits, adding/subtracting from numbers, or inserting boundary values (e.g.,
MAX_INT). 低级和通用:例如翻转位、从数字中加/减或插入边界值(例如,'MAX_INT')。 - High-level and specific: Such as adding, removing, or swapping entire elements in a structured file (like removing a table from an HTML document). 高级和具体:例如添加、删除或交换结构化文件中的整个元素(例如从 HTML 文档中删除表格)。
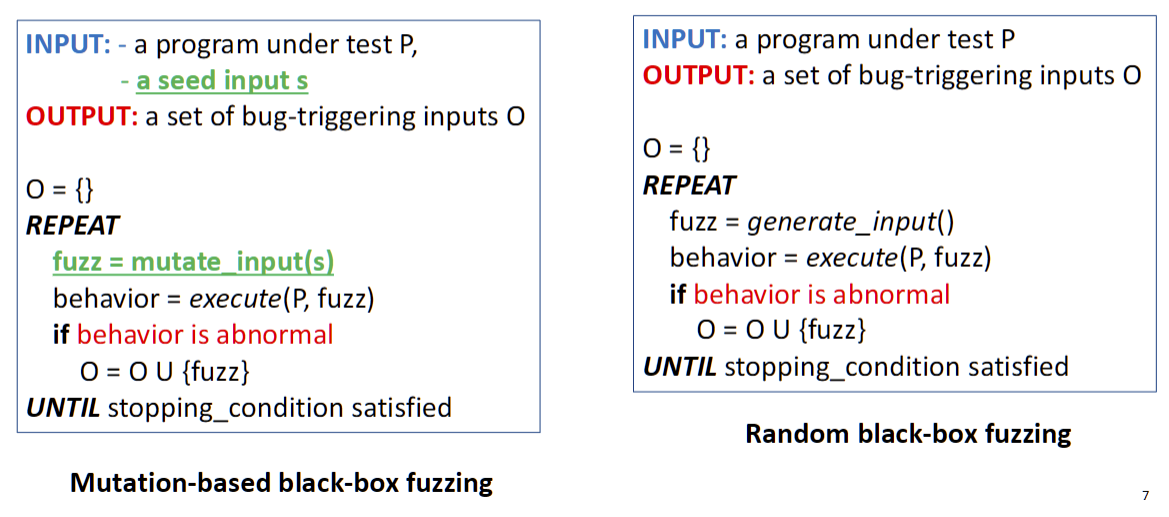 The pseudocode and a sample bash script show the key difference from random fuzzing. Instead of generating an input from scratch (
The pseudocode and a sample bash script show the key difference from random fuzzing. Instead of generating an input from scratch (generate_input()), the fuzzer calls a mutate_input(s) function that takes a seed input s as its starting point. The script uses a tool called radamsa to perform this mutation.伪代码和示例 bash 脚本显示了与随机模糊测试的主要区别。模糊器不是从头开始生成输入 (“generate_input()”,而是调用一个 'mutate_input(s)' 函数,该函数以种子输入 's' 为起点。该脚本使用一种名为“radamsa”的工具来执行此突变。
The success of mutation-based fuzzing depends heavily on having good quality seed inputs. More importantly, it struggles with highly structured file formats that have integrity checks (like checksums) or semantic relationships (like a field that specifies the length of another field). A simple, random mutation like flipping a bit will almost certainly invalidate these checks, causing the program to reject the input immediately. This means the fuzzer can't test the deeper, more complex logic of the program. 基于突变的模糊测试的成功在很大程度上取决于拥有高质量的种子输入。更重要的是,它难以处理具有完整性检查(如校验和)或语义关系(如指定另一个字段长度的字段)的高度结构化文件格式。一个简单的随机突变(例如翻转一点)几乎肯定会使这些检查失效,导致程序立即拒绝输入。这意味着模糊器无法测试程序更深层次、更复杂的逻辑。
- PNG file format. A PNG file isn't just a random stream of bytes; it's a highly structured format with a signature, data chunks, and integrity constraints like length fields and CRC checksums. A simple mutation-based fuzzer that is unaware of this structure will create corrupted files that are rejected by the parser, preventing effective testing.PNG 文件不仅仅是随机的字节流;它是一种高度结构化的格式,具有签名、数据块和完整性约束,如长度字段和 CRC 校验和。一个简单的基于突变的模糊器不知道这种结构,将创建被解析器拒绝的损坏文件,从而阻止有效的测试。
Generation-Based Black-Box Fuzzing
- Generation-based fuzzing is presented as the solution to the problems of mutation-based fuzzing. Instead of modifying existing inputs, this technique generates inputs from scratch using an input model or grammar that explicitly defines the structure and rules of the input format.基于生成的模糊测试被提出为基于突变的模糊测试问题的解决方案。该技术不是修改现有输入,而是使用显式定义输入格式的结构和规则的输入模型或语法从头开始生成输入。
- Peach fuzzer is introduced as a popular generation-based fuzzer. It uses an input model (typically an XML file) to understand the file structure. It can then generate new, structurally valid inputs that explore different values and combinations within that structure.Peach Fuzzer 作为一种流行的基于世代的模糊器而推出。它使用输入模型(通常是 XML 文件)来理解文件结构。然后,它可以生成新的、结构上有效的输入,探索该结构中的不同值和组合。
- Peach data model (the grammar) for the PNG format. The XML file defines each part of the file, such as a generic "Chunk". Critically, it includes
<Relation>tags that enforce integrity constraints. For example, one relation specifies that the "Length" field must be equal to the actual size of the "Data" block, and another uses aCrc32Fixupto ensure the checksum is always calculated correctly. By understanding these rules, the fuzzer can generate valid inputs that test the program's logic, not just its initial parser.
Peach 数据模型(语法)用于 PNG 格式。XML 文件定义了文件的每个部分,例如通用“块”。至关重要的是,它包括 <Relation> 强制执行完整性约束的“”标签。例如,一个关系指定“Length”字段必须等于“Data”块的实际大小,另一个关系使用“Crc32Fixup”来确保校验和始终正确计算。通过理解这些规则,模糊器可以生成有效的输入来测试程序的逻辑,而不仅仅是其初始解析器。