Week 7: Introduction to Security Testing
Testing Methodologies
| Methodology | Test Design | Test Execution | Test Oracle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Testing | Manual | Manual | Human oracle |
| Test Automation | Manual | Automated (via scripts) | Human oracle (encoded in scripts) |
| Automated Testing | Automated | Automated | Automated |
Slides 6-17: Understanding Software Vulnerabilities
A software vulnerability is defined as a fault that an attacker can exploit to compromise a system's security. This could allow them to gain unauthorized access, steal data, corrupt information, or crash the system. SQL injection and buffer overflows are given as classic examples. 软件漏洞被定义为攻击者可以利用的故障来危害系统的安全。这可能允许他们获得未经授权的访问、窃取数据、损坏信息或使系统崩溃。SQL 注入和缓冲区溢出作为经典示例给出。
2022 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Weaknesses, a real-world list that highlights the most common and critical types of vulnerabilities found in software. The top weaknesses include Out-of-bounds Write, Cross-site Scripting (XSS), and SQL Injection.
Example 1 - SQL Injection:
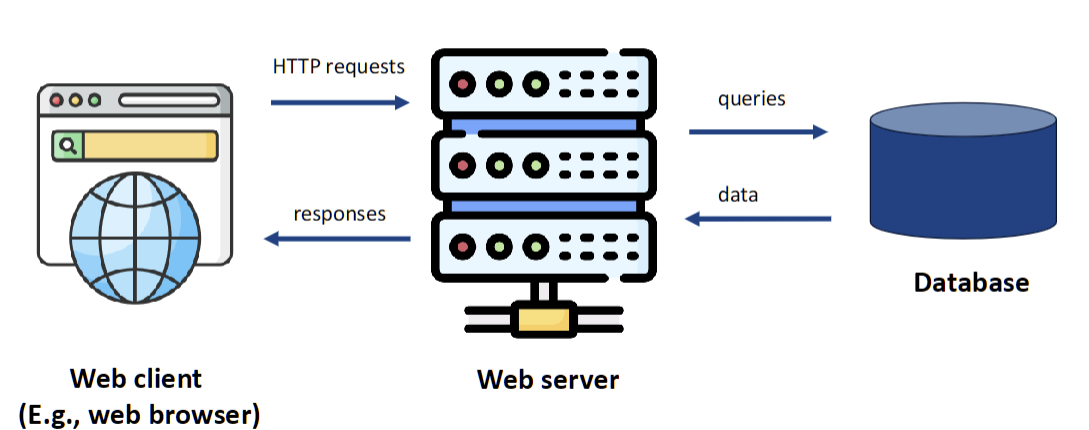
- This is a vulnerability where an attacker injects malicious SQL code into a user input field.
- If a developer constructs a query by simply pasting user input (like
'$EMAIL_ADDRESS') into a string, an attacker can provide a specially crafted input likemyemail@somedomain.com' OR '1=1. - This tricks the database into executing the query
...WHERE email = 'myemail@somedomain.com' OR '1=1', which always evaluates to true, potentially giving the attacker access to all data in the table.
Example 2 - Buffer Overflow:
- A buffer overflow happens when a program tries to write more data into a fixed-size memory buffer than it can hold .当程序尝试将比其可以容纳的数据更多的数据写入固定大小的内存缓冲区时,就会发生缓冲区溢出。
- The excess data overflows and overwrites adjacent memory locations. A vulnerable C function like
strcpy()is often the cause because it doesn't check the destination buffer's size.多余的数据会溢出并覆盖相邻的内存位置。像 'strcpy()' 这样易受攻击的 C 函数通常是原因,因为它不检查目标缓冲区的大小。 - By carefully crafting the oversized input, an attacker can overwrite the function's return address on the stack, hijacking the program's control flow and forcing it to execute malicious code. 通过精心制作超大的输入,攻击者可以覆盖堆栈上函数的返回地址,劫持程序的控制流并强制其执行恶意代码。
Other Famous Vulnerabilities:
- Heartbleed: A vulnerability in OpenSSL where an attacker could send a malicious "heartbeat" request, tricking the server into sending back random chunks of its private memory, which could contain sensitive data like passwords or private keys. OpenSSL 中的一个漏洞,攻击者可以发送恶意“心跳”请求,诱骗服务器发回其私有内存的随机块,其中可能包含密码或私钥等敏感数据。
- Log4Shell: A critical vulnerability in the Log4j logging library where simply logging a malicious string could cause the server to connect to an attacker's server and execute arbitrary code.Log4j 日志记录库中的一个严重漏洞,只需记录恶意字符串即可导致服务器连接到攻击者的服务器并执行任意代码。
Introduction to Fuzzing
Software vulnerabilities can be discovered through several methods, including manual code inspection, static analysis, and dynamic analysis. Fuzzing is presented as a primary dynamic analysis technique. 软件漏洞可以通过多种方法发现,包括手动代码检查、静态分析和动态分析。模糊测试是一种主要的动态分析技术。
The term "fuzzing" was coined in 1988 by Prof. Barton Miller. The idea came from observing that random line noise sent over a modem connection during a thunderstorm was causing UNIX utility programs to crash.“模糊测试”一词是由 Barton Miller 教授于 1988 年创造的。这个想法来自观察到在雷暴期间通过调制解调器连接发送的随机线路噪声导致 UNIX 实用程序崩溃。
Fuzzing is formally defined as repeatedly running a program with automatically generated inputs that may be syntactically or semantically malformed. The core components are: 模糊测试被正式定义为重复运行一个程序,其中包含自动生成的输入,这些输入可能在语法或语义上是错误的。核心组件是:
- A Fuzzer that generates inputs.生成输入的 Fuzzer。
- The Program Under Test (PUT).被测程序 (PUT)。
- A Bug/Fault Detector that monitors the PUT for crashes or other abnormal behavior.一个错误/故障检测器,用于监控 PUT 是否存在崩溃或其他异常行为。
Fuzzers categories:
- Generation-based (creating inputs from scratch) vs. Mutation-based (modifying existing valid inputs).基于生成(从头开始创建输入)与基于突变(修改现有有效输入)。
- Dumb (unaware of input structure) vs. Smart (aware of input structure, like file formats). 愚蠢(不知道输入结构)与智能(知道输入结构,如文件格式)。
- Black-box (no knowledge of the program's internals), Grey-box (some knowledge, like code coverage), or White-box (full knowledge from source code analysis). 黑盒(不了解程序的内部结构)、灰盒(一些知识,如代码覆盖率)或白盒(源代码分析的全部知识)。
Random fuzzing
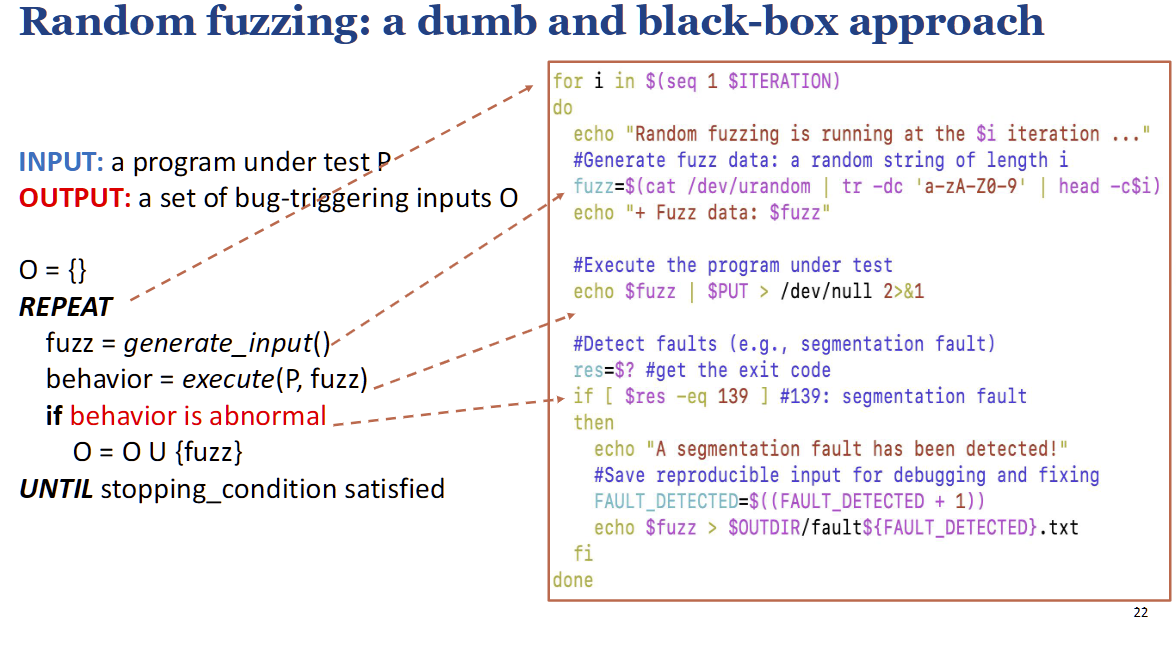 Random fuzzing is the simplest approach: a dumb, black-box technique. The process is a simple loop: generate a random input, execute the program with it, and check for abnormal behavior (like a crash). The slide shows a bash script that does this by generating random strings and checking the program's exit code for a segmentation fault. 随机模糊测试是最简单的方法:一种愚蠢的黑盒技术。该过程是一个简单的循环:生成一个随机输入,用它执行程序,并检查异常行为(如崩溃)。幻灯片显示了一个 bash 脚本,它通过生成随机字符串并检查程序的退出代码是否存在分段错误来实现此目的。
Random fuzzing is the simplest approach: a dumb, black-box technique. The process is a simple loop: generate a random input, execute the program with it, and check for abnormal behavior (like a crash). The slide shows a bash script that does this by generating random strings and checking the program's exit code for a segmentation fault. 随机模糊测试是最简单的方法:一种愚蠢的黑盒技术。该过程是一个简单的循环:生成一个随机输入,用它执行程序,并检查异常行为(如崩溃)。幻灯片显示了一个 bash 脚本,它通过生成随机字符串并检查程序的退出代码是否存在分段错误来实现此目的。 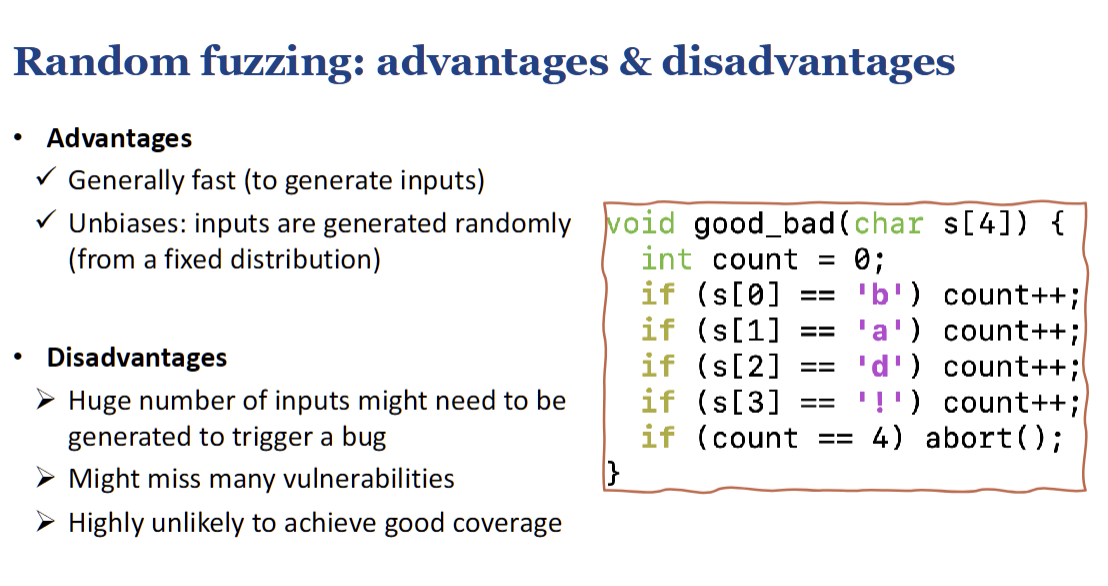
- Advantages: It's fast and unbiased. 它快速且公正。
- Disadvantages: It's very inefficient. It may require a huge number of inputs to trigger a bug and is highly unlikely to achieve good code coverage. The example code shows that to trigger an
abort(), the fuzzer would have to randomly guess the exact string "bad", which has a very low probability. 效率非常低。它可能需要大量输入才能触发错误,并且极不可能实现良好的代码覆盖率。示例代码显示,要触发“abort()”,模糊器必须随机猜测确切的字符串“bad”,这的概率非常低。