Distributed and Parallel Computing Systems
Compute Scaling
Vertical Computational Scaling
- Have faster processors 拥有更快的处理器
- Switch your n GHz CPU for a 2n GHz one = 2x faster 把频率搞高一点
- Easy to do, but costs more 做起来容易,但成本更高
- Limits of fundamental physics/matter (nanoCMOS)
堆配置
提高店铺的出单效率:把原先店铺重新装修,购买好的装备,聘请好的制作师傅
Horizontal Computational Scaling
- Have more processors
拥有更多处理器 - Easy to add more; cost increase not so great
易于添加更多;成本增加不是那么大 - But harder to design, develop, test, debug, deploy, manage, understand 但更难设计、开发、测试、调试、部署、管理、理解
堆数量
提高店铺的出单效率:开两家同样的店铺
Quote
HTC far more important than HPC
| Architecture | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Single machine multiple cores 单机多核 | Typical laptop/PC/server these days. 如今典型的笔记本电脑/PC/服务器。 | N/A |
| Loosely coupled collection/cluster of machines 松散耦合的机器集合/集群 | Pooling/sharing of resources. Can be dedicated or available only when not in use by others. 资源池化/共享。可以是专用的,也可以仅在其他人不使用时可用。 | Web services, Condor, Seti@home, Boinc |
| Tightly coupled cluster of machines 紧密耦合的机器集群 | Typical High-Performance Computing (HPC)/High-Throughput Computing (HTC) set-up. Consists of many servers in the same rack/server room, often with fast message-passing interconnects. 典型的高性能计算 (HPC)/高吞吐量计算 (HTC) 设置。由同一机架/服务器机房中的许多服务器组成,通常具有快速消息传递互连。 | SPARTAN, NCI |
| Widely distributed clusters of machines 广泛分布的机器集群 | Related to distributed systems more generally. 更普遍地与分布式系统相关。 | UK NGS, EGEE |
| Hybrid combinations of the above 上述的混合组合 | Leads to many challenges with distributed systems, such as shared state (or lack thereof) and message passing paradigms (dangers of delayed/lost messages). 导致分布式系统面临许多挑战,例如共享状态(或缺乏共享状态)和消息传递范式(消息延迟/丢失的危险)。 | N/A |
High performance Computing
- 通过构建高性能的集群系统,将大量的计算资源集中在一个相对集中的环境中进行统一管理和使用,资源通常属于同一组织或机构,具有同构性,即硬件和软件环境相对统一,便于管理和调度
- Cluster Computing是实现HPC的重要技术手段之一
Moore's Law
The number of transistors in an IC doubles about every two years.
Info
整体趋势: 性能提升,成本下降
Parallel Computing
Terminology
Amdahl's Law
Info
程序中可串行化部分(无法并行处理的部分)的比例决定了并行计算的性能上限
SpeedUp Formula
The speedup of a program from parallelization is calculated based on the ratio of the sequential time (Tseq) to the parallel time (Tpar). The sequential time is simply T. The parallel time is the sum of the time for the serial fraction (1-α)T and the time for the parallel fraction α(T/N). The overall speedup is given by the formula:
Theoretical Maximum SpeedUp
As the number of processors (N) gets very large, the term α/N approaches 0. This means the total speedup tends towards a limit defined by the serial portion of the code. 随着处理器 (N) 的数量变得非常大,“α/N”接近 0。这意味着总加速比趋向于代码的 serial 部分定义的限制。
Example
Thus, if 95% of the program can be parallelized (
This means the maximum speedup is 20x, no matter how many processors are used. For instance, if the non-parallelisable part (5%) takes 1 hour to run, then no matter how many cores you throw at it, the entire program will never complete in less than 1 hour. 这意味着无论使用多少个处理器,最大加速都是 20x。例如,如果不可并行化部分 (5%) 需要 1 小时才能运行,那么无论你投入多少个内核,整个程序都不会在 1 小时内完成。
Gustafson-Barsis's Law
Info
可以通过增大问题规模和处理器个数,达到任意加速比
Speed up S using N processes is given as a linear formula dependent on the number of processes and the fraction of time to run sequential parts. Gustafson's Law proposes that programmers tend to set the size of problems to use the available equipment to solve problems within a practical fixed time. Faster (more parallel) equipment available, larger problems can be solved in the same time.
使用 N 个进程加速 S 是一个线性公式,取决于进程数和运行连续部件的时间分数。古斯塔夫森定律 (Gustafson's Law) 提出,程序员倾向于设置问题的大小,以便在实际的固定时间内使用可用的设备来解决问题。更快(更并行)的设备可用,更大的问题可以同时解决。
Difference and Aim
并无矛盾,讨论的场景不同
| Amdahl | Gustafson | |
|---|---|---|
| 核心假设 | 问题规模固定 | 总执行时间固定,但是问题规模可以拓展 |
| 关注点 | 加速比受限于穿行部分的比例 | 加速比随着问题的规模的拓展而增长 |
| 视角 | 悲观的,强调性能瓶颈 | 乐观,强调并行计算的潜力 |
| 使用场景 | 固定大小问题的优化 | 可拓展问题的性能预测,比如科学计算 |
Computer Architecture
Flynn's Taxonomy
| Single instruction | Multiple instruction | |
|---|---|---|
| Single data | 在指令或数据流中没有并行性的顺序计算机 单个控制单元 (CU/CPU) 从内存中获取单个指令流。然后,CU/CPU 生成适当的控制信号,以指示单个处理元件对单个数据流进行action,即一次执行一个action。 传统执行模式 效率不高 冯·诺依曼计算机的基本思想 | 并行计算架构,其中许多功能单元 (PU/CPU) 对同一数据执行不同的action 例如,在同一数据流上运行多个错误检查过程 不常见, 容错系统中的数据处理和校验 |
| Multiple data | 1. 同时对多个数据点执行相同action的多个处理元素 2. 重点是数据级并行性,即许多并行计算,但在给定时刻只有一个进程(指令) 3. 许多现代计算机使用 SIMD 指令,例如,提高多媒体使用的性能,例如用于图像处理 较为常见 数据并行 适合图像和音频处理等 | 1. 异步和独立运行的处理器数量 2. 在任何时候,不同的处理器都可能对不同的数据片段执行不同的指令 3. 计算机可以是共享内存或分布式内存类别 4. 取决于 MIMD 处理器访问内存的方式 超级计算机 大型复杂的分布式系统 |
Approaches for Parallelism
Where and how
- Explicit vs Implicit parallelism
- openMP / MPI
- Hardware
- Operating System
- Software/Applications
- Some or all of these
Explicit vs Implicit Parrallelisation
| Implicit Parallelism | Explicit Parallelism |
|---|---|
| 由并行语言和并行编译器提供支持,这些编译器负责识别并行性、计算调度和数据放置 | 1. 在这种方法中,程序员负责大部分并行化工作,例如任务分解、将任务映射到处理器、进程间通信 2.此方法假定用户是特定应用程序如何利用并行性的最佳判断者 通常,实现并非易事 |
Open Multi-Processing (OpenMp)
- 广泛使用的 API 用于共享内存并行编程
- 提供的功能可以更轻松地为多核和多处理器系统编写并行程序
- 并行构造 定义多个线程并发执行代码的并行区域
- 工作共享结构 在线程之间划分工作的机制
Message Passing Interface (MPI)
- Widely adopted approach for message passing in parallel systems
- Mappings to major languages Fortran
- Standardised, widely adopted, portable, performant
- Parallelism = user's problem
- Key MPI functions
MPI_INIT: initiate MPI computationMPI_Finalize: terminate computationMPI_COMM_SIZE: determine number of processorsMPI_COMM_RANK: determine my process identifierMPI_SEND: send a messageMPI_RECV: receive a message
from mpi4py import MPI
import os
import json
# Initialize the MPI communicator. COMM_WORLD includes all the processes in the MPI job.
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
# Get the rank (unique ID) of the current process within the communicator.
rank = comm.Get_rank()
# Get the total number of processes (the size of the communicator).
size = comm.Get_size()
# This block is executed only by the master process (rank 0).
if rank == 0:
# The master process gets the total size of the input file (file_name must be defined elsewhere).
ndjson_size = os.path.getsize(file_name)
else:
ndjson_size = None
ndjson_size = comm.bcast(ndjson_size, root=0)
# 它将数据从一个进程发送到指定通信器中的所有其他进程。
reading_size = ndjson_size // size
start = rank * reading_size
if rank == size - 1:
end = ndjson_size
else:
end = (rank + 1) * reading_size
time_dict = {}
account_dict = {}
## After processing the data
# 将所有进程的 account_dict 收集到主进程 (root=0) 上
all_time_dict = comm.gather(time_dict, root=0)
all_account_dict = comm.gather(account_dict, root=0)Hardware
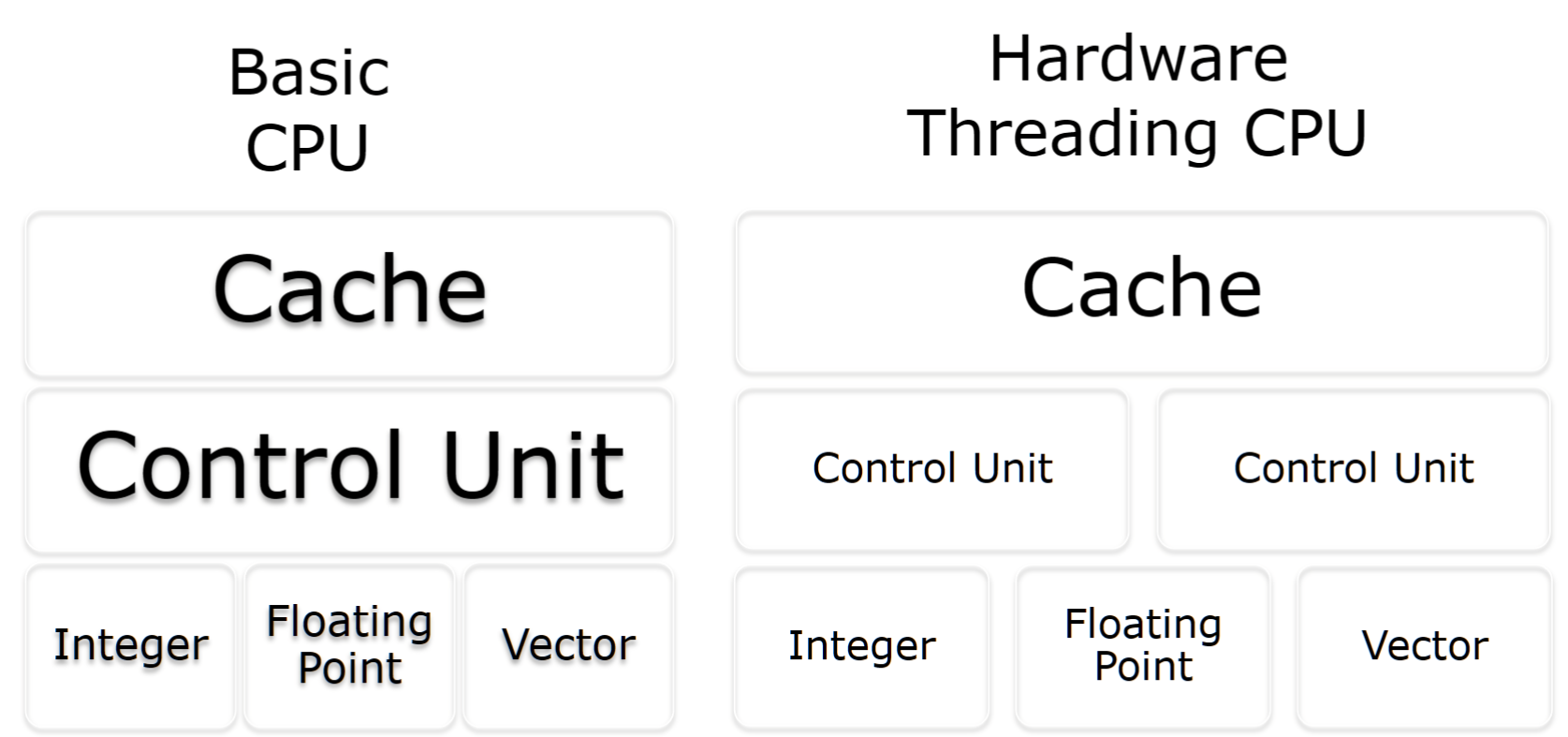
Cache
Cache – much faster than reading/writing to main memory; instruction cache, data cache (multi- level) and translation lookaside buffer used for virtual-physical address translation (more later on Cloud and hypervisors).
缓存 – 比读/写主内存快得多;指令缓存、数据缓存(多级别)和用于虚拟物理地址转换的转换后备缓冲区(稍后将详细介绍云和虚拟机管理程序)。
Hardware Threading
Parallelisation by adding extra CPU to allow more instructions to be processed per cycle. Usually shares arithmetic units. Heavy use of one type of computation can tie up all the available units of the CPU preventing other threads from using them.
通过增加额外的CPU部件(如控制单元),让一个CPU核心能同时处理更多指令,但计算单元是共享的。 过度使用一种计算可能会“霸占”所有计算单元。
Multi-Core
Multiple cores that can process data and ( in principle!!!) perform computational tasks in parallel. Typically share same cache, but issue of cache read/write performance and cache coherence. Possibility of cache stalls (CPU not doing anything whilst waiting for caching); many chips have mixture (L1 cache on single cores; L2 cache on pairs of cores; L3 cache shared by all cores); typical to have different cache speeds and cache sizes (higher hit rates but potentially higher latency).
将多个独立的CPU核心集成在一块芯片上,可以真正地并行执行计算任务。 它们通常会共享部分缓存(如L3缓存),因此带来了缓存一致性(cache coherence)的挑战。
Symmetric Multiprocessing - SMP
Two (or more) identical processors connected to a single, shared main memory, with full access to all I/O devices, controlled by a single OS instance that treats all processors equally. Each processor executes different programs and works on different data but with capability of sharing common resources (memory, I/O device, ...). Processors can be connected in a variety of ways: buses, crossbar switches, meshes. More complex to program since need to program both for CPU and inter-processor communication (bus).
将两个或多个相同的处理器连接到单一的共享主内存上。 每个处理器可以运行不同的程序,处理不同的数据,但也能访问共同的资源。
Operating System Parallelism Approaches
- Most modern multi-core operating systems support different forms of parrallelism
- parallel or interleaved semantics A || B or A ||| B
- Compute parallelism
- processes - uses to realise tasks, structure activities, 用于实现任务、构建活动......
- Threads
- Native threads
- Fork, spawn, join
- Green threads
- Scheduled a virtual machine instead of natively by the OS 计划虚拟机,而不是由 OS 本机计划
- Native threads
- Data parallelism
- Caching
- OS implies "a" computer
Software Parallelism Approaches
很多语言现在支持一大部分的平行/并行特点
- e.g. Threads thread pool ...
有可能出现的问题
- Deadlock process involved constantly for each other 不断相互参与的过程
- livelock constantly change with regard to one another, but none are progressing 彼此之间不断变化,但没有一个进步
Challenge of big data
- Consistency, Availabilities, Partition tolerance 一致性、可用性、分区容错能力
- e.g. ElasticSearch
Distributed System and Parallel Computing
The Assumption of Distributed Systems
The network is reliable?
- 数据无法确认是否已发送
- 数据无法确认是否是按顺序发送
- 网络栈中底层级无法保证能够避免以上问题
Latency is zero?
- 如果我发一条消息,那他会马上到达对方那里吗?
- 距离, 物理限制
- 可以用route (traceroute) 查看
- In a system with many nodes/hops each link can have different latencies
- 在具有许多节点/跃点的系统中,每个链路可以具有不同的延迟
- Next hop behaviour can be challenging 下一跃点行为可能具有挑战性
- Explored in active networking technologies, software defined networking,... 在主动网络技术、软件定义网络中进行了探讨,...
Bandwidth is infinite?
- 我可以在节点之间发任意数量的数据?
- 网络容量是提前仔细规划好的
The network is secure?
- 有些人一直在试密码,SQL攻击
- 会有人一直攻击我
- 中间人攻击
- 有人黑进了我的其中一个节点 e.g. 暴力攻击,病毒
- 有人偷了我的硬件设施
Topology doesn't change?
- 路由变换
- 延迟的变化
- 连接中断?
There is one administrator
- 权限管理
- 防火墙变化
- 责任判定
Transport cost is not zero
- 数据传输需要硬件支持, 花钱买aws ec2
The network is not homogenous
- 设备类型差异
- 协议差异
- 网络性能差异
Time is not ubiquitous
- 时钟同步现需要依赖网络延迟,精度有差异
Partitioning model
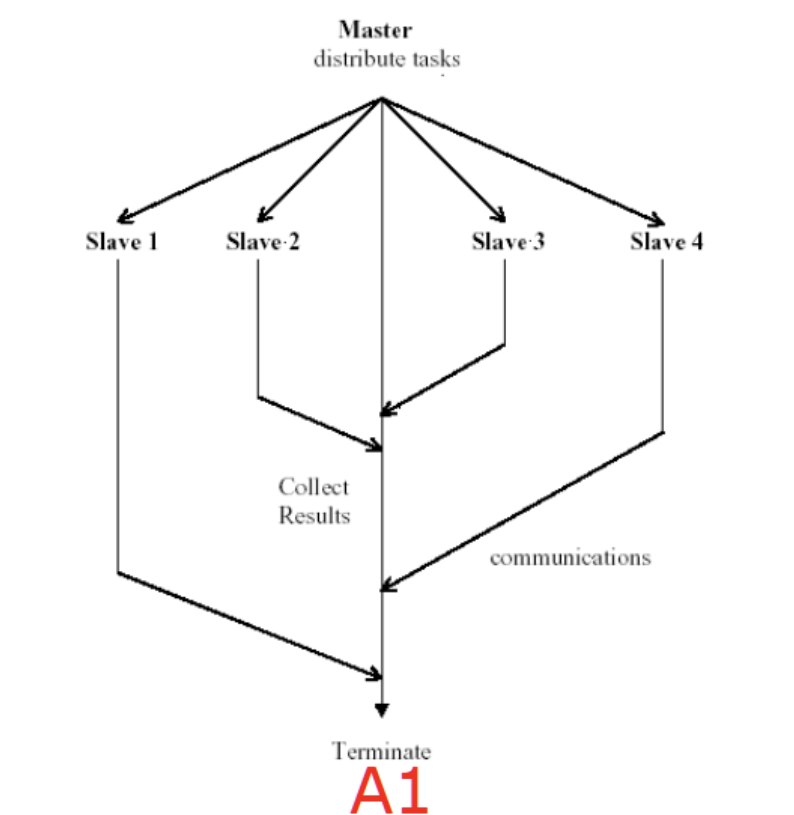
Master/slave
Info
- Pros
- 主节点只负责分解任务和结果汇总
- 易于实现管理,任务调度和监控方便
- Cons
- 主节点存在性能瓶颈和单点故障的问题
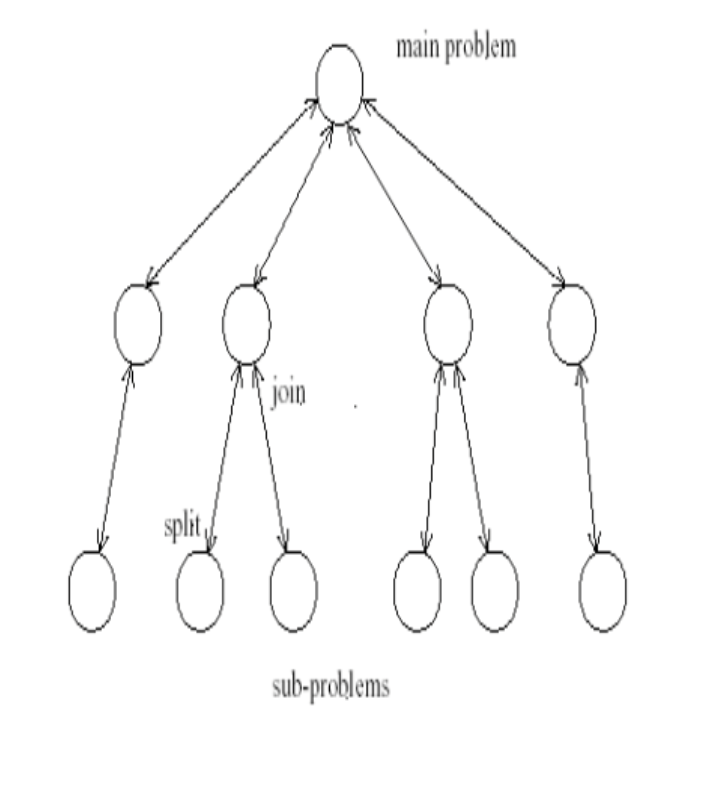
Divide and Conquer
Info
- 将任务分解为独立且结构相同的子问题进行求解,再合并问题
- 侧重算法设计和问题分解的策略方向
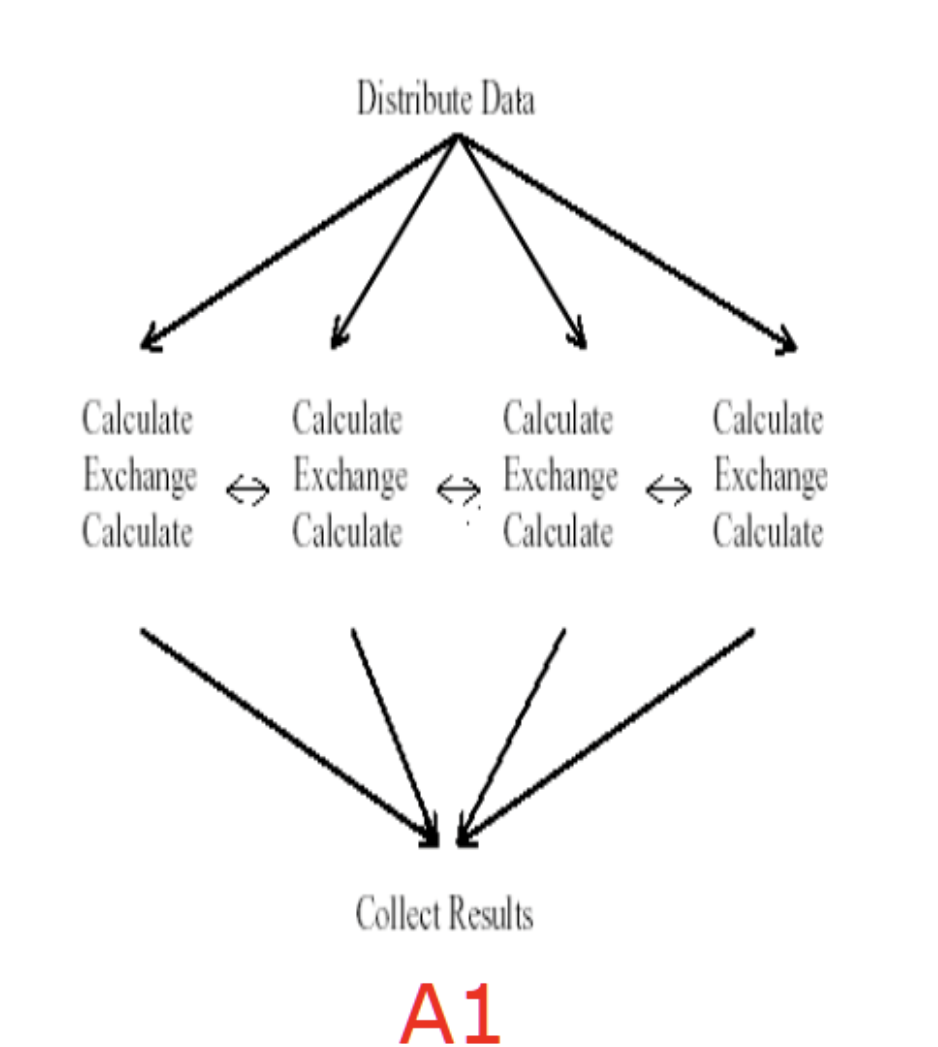
Single Program Multiple Data
Info
- 所有节点执行相同的程序但操作的数据不同
- 编程简单,不需要任务分配,各单元独立无依赖
Data pipelining
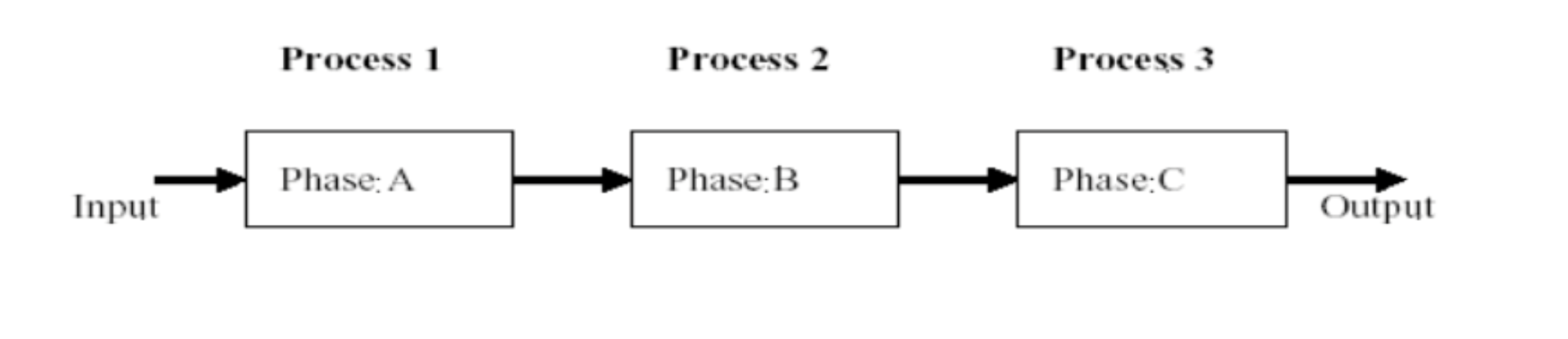
Info
计算任务分解成各个阶段,依次执行 可以接受持续数据据输入,系统功能性更强更复杂,阶段效率影响流水线效率
Workshop
社交媒体数据的挑战
- 隐私与监控: 涉及对人们的实时追踪和监控 。
- 假新闻: 误导人们变得前所未有地容易 。
- 大数据挑战: 涉及到数据的体量 (Volume)、速度 (Velocity)、多样性 (Variety) 和真实性 (Veracity) 。
AIO平台的核心功能 该平台主要有四大核心分析能力,你可以在其研究仪表盘 (Research Dashboard) 中找到 。
- 数据聚合 (Data Aggregation): 能够按地点、时间、季节性和语言等维度,通过多种图表将数据可视化 。它还可以在不同地理级别(如州、首府城市统计区、郊区)比较聚合数据 。
- 主题图谱 (Topic Graph): 基于特定日期的主题集群构建网络图 。图中的节点代表一天内的主题集群,边则通过主题间的共同术语数量来连接相似的主题 。
- 术语分析 (Term Analysis): 可以与基于每日频率构建的词嵌入模型互动,以研究特定术语之间随时间变化的语义关系 。
- 文本搜索 (Text Search): 使用全文搜索来探索感兴趣的社交媒体内容,并且可以将相关帖子的URL导出为CSV文件 。
AIO平台的实际应用案例 讲座中通过两个生动的案例来展示AIO的功能:
- COVID-19疫苗情绪分析: 分析了关于不同疫苗(如辉瑞、莫德纳、阿斯利康)的帖子数量和情绪(正面、负面、中性) 。
- 德约科维奇公众舆论事件: 通过时间线追踪了在2022年1月围绕网球明星诺瓦克·德约科维奇签证风波的公众舆论变化 。
Exam Questions
Define Gustafson-Barsis’ law for scaled speed-up of parallel programs.
直接给出每个变量的定义 并写出公式+一句话解释
A parallel program takes 128 seconds to run on 32 processors. The total time spent in the sequential part of the program is 12 seconds. What is the scaled speedup?
alpha =
Scaled speed up =
Scaled speed up = -29.9
Discuss the major trends in research and research computing over the last 20 years that have led to the emergence of Cloud computing
根据前面讲的Distributed System到Grid Computing到Cloud Computing的演变讲 每个阶段的目标是什么 新的技术解决了什么困难或问题 带来了什么新的挑战