Project Tracking and Control
- simple methods to track
- Periodic meetings where team members report progress.
- Evaluating the results of reviews and audits conducted as part of the software engineering process.
- Tracking formal project milestones.
- Comparing actual start dates with scheduled start dates.
- Meeting engineers and having informal discussions.
- Using a formal method like earned value analysis.
Earned Value Analysis EVA
- EVA can be used to:
- report current/past project performance
- predict future project performance based on current/past performance
- Results can be expressed in dollars and/or percentage
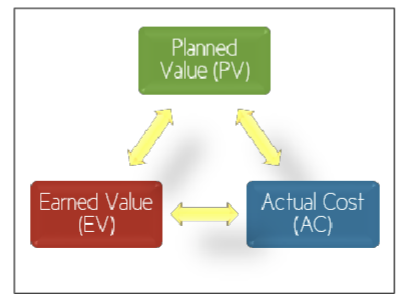
EVA calculation
- Planned Value (PV)
- The authorized budget assigned to scheduled work. It represents the portion of the approved cost estimate planned to be spent on a given activity during a specific time period.
- The Earned Value (EV)
- The value of the work actually completed, expressed in terms of the approved budget for that work.
- Actual Cost (AC)
- The total cost incurred for the work completed on a specific activity during a given time period.
- Schedule Variance Analysis
- Uses EV and PV to calculate a variance to the project schedule.
- Schedule Variance
- Expressed in currency units (e.g., dollars). A positive value indicates ahead of schedule; negative means behind.
- Schedule Performance Index
- A ratio (i.e., a fraction). An
indicates better than planned schedule performance; means worse
EVA metrics example !!
