Formal Project Scheduling
Project Schedule
- One of the important artefacts generated during the project planning phase.
- Is used and maintained throughout the project to monitor and track project progress.
- It is a living document
- Answers two important questions
- How long will the system take to develop
- How much will it cost
- Project Schedule contains
- Duration and dependencies for each task
- People and physical resources for each task
- Milestone and deliverables
- Project Timeline
- Gantt charts -> bar chart shows schedule against against calendat
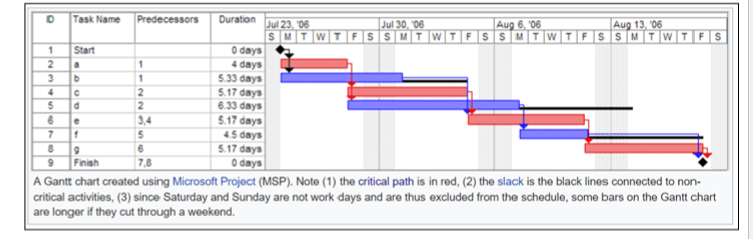
- PERT(Program evaluation and review techinique charts) chart -> an activity network shows dependency and critical path
Develop Project Schedule
- Breakdown the task into small chunks you can deal with - Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
- Identify the interdependencies between the broken-down tasks and develop a task network.
- Estimate the effort and the time allocation for each task.
- Allocate resources for tasks and validate effort.
- Develop the project schedule.
WBS
Planning and executing large tasks is challenging:
- Estimating the time and resources.
- Identifying interim goals and deliverable.
- Progress monitoring.
Solution is to break the task down to manageable units:
- Each task should have a specific outcome or a deliverable.
- This creates a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
Fishbone Diagram aka cause-effect diagram
Used in software project management as a tool for identifying, sorting, and displaying possible causes of a specific problem or quality characteristic
Problem Solving:
- Helps teams identify the root cause of issues affecting project quality, deadlines, or budget.
Visualization:
- Visually organizes the causes of project issues into categories, making it easier to brainstorm and discuss these issues.
Team Collaboration:
- Engages various team members in the problem-solving process.
Focus on Factors:
- Common categories in software projects might include People, Processes, Tools, and External influences etc.
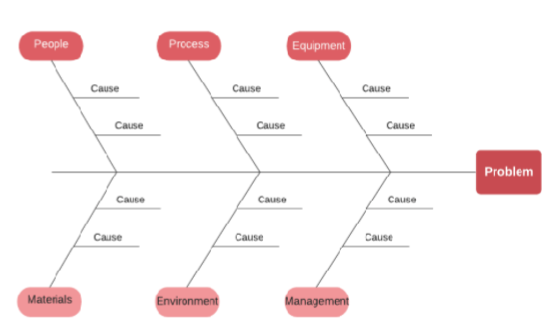
- Common categories in software projects might include People, Processes, Tools, and External influences etc.
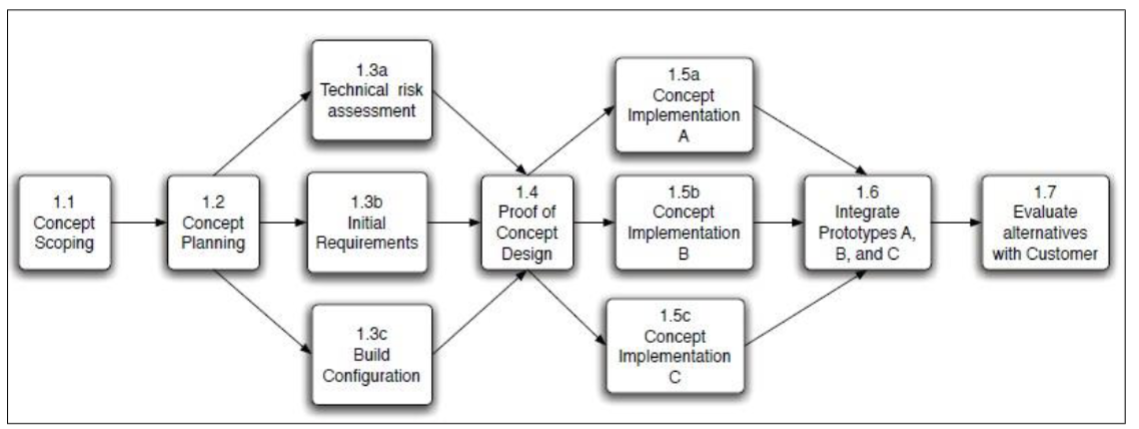
Identifying Task Dependencies
constrained -> depends on another task
unconstrained -> the task can start at any time
Dependencies are caused by:
- a task needing a work product of another task.
- a task needing resources used by another task
Effort-time Estimation
A common measure for estimating the effort for software is person-months.
- The time in months for a single person working full time to complete the task.
Three-point estimating is a widely-used technique used to estimate the duration (or cost) of a task with a more refined approach, than only using a single-point estimate.
- It considers uncertainty and the risk of potential variation in task estimates.
- But there are different types of three-point estimation
The two most common methods of three-point estimating are the Triangular Distribution and the PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) Distribution
- Triangular Distribution
Calculates the average of the three estimates. Less reliable.
O - optimistic time
P - pessimistic time
M - most likely time
PERT Distribution
More commonly used due to its higher weighting of the most likely scenario (4M), weights the most likely estimate more heavily:
O - optimistic time
P - pessimistic time
M - most likely time
How do we determine O, P and M?
This often comes through experience/expertise in having worked on previous similar projects.
Often it is an well-informed best guess.
Resource Allocation
- if the effort and time are known, get
- Assigning people to tasks:
- Although computing the number of personnel required for each task appears simple, resource allocation is complicated task.
- The project manager has to carefully consider the expertise of the people, and the availability of them for tasks, which might require validation and adjustment of the schedule
Develop the project Schedule
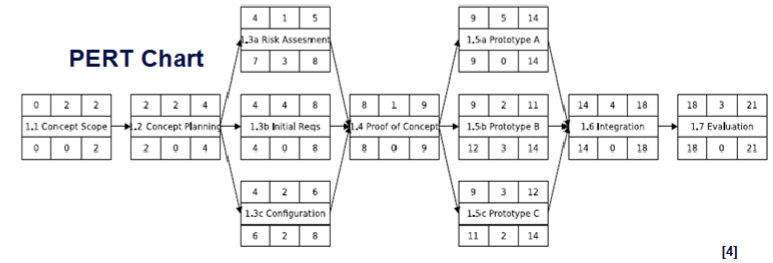
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) chart:
- A task network which shows the dependencies along with time related information and the critical path.
- PERT analysis helps:
- Understand the characteristics of the project that will let project managers do scheduling trade-offs.
- Perform critical path analysis.
- Monitor project progress and re-plan

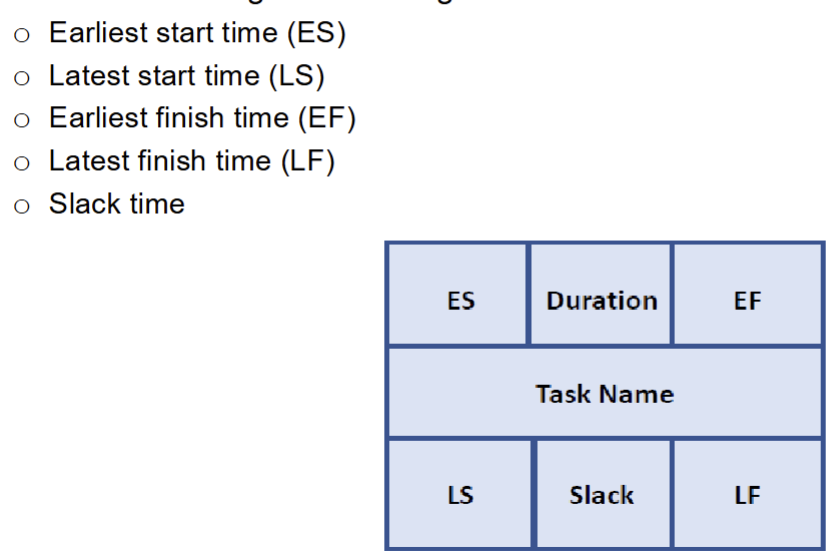
Critical Path Methods
- critical path
- Path with the longest duration.
- Activities on the critical path have a total free slack of 0.
- A delay in any of the activities in the critical path will cause the project to delay
- Crashing the project schedule
- Shortening the total duration of the project by shortening the critical path. By removing the dependencies between activities in the critical path; or
- Shortening the duration of activities in the critical path.